Cart (0 Items)
Your cart is currently empty.
View ProductsIt looks like you are visiting from outside the EU. Switch to the US version to see local pricing in USD and local shipping.
Switch to US ($)
You need to detect small amounts of your target? Let us develop your own sandwich ELISA! We guarantee that your sandwich ELISA will detect your target even in complex samples (sera, tissue homogenates, cell lysates) because we master all the development steps from antigen design to the pilot kit production (validated with your own samples).
We guarantee that you will get a fully functional Sandwich ELISA.
Provide us hundreds of samples (sera, tissue homogenates, cell lysates). We optimize your sandwich ELISA in real conditions!
Our fully integrated solutions include the whole development of your sandwich ELISA from antigen design to pilot kit production.
You get access to our unique expertise and technical capabilities in sandwich ELISA design for various applications.
We generate polyclonal or monoclonal antibodies depending on your requirements.
Our sandwich ELISA service is fully custom. It can include monoclonal antibody generation by hybridoma or phage display.
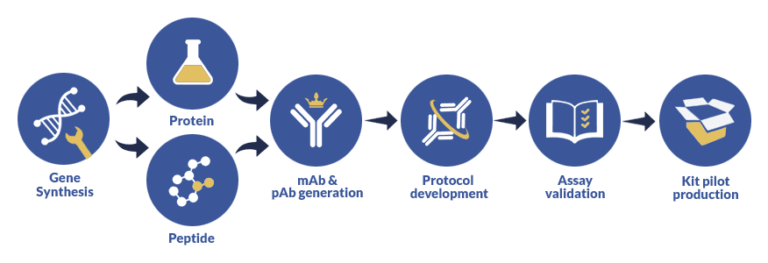
Having helped a large number of corporations, laboratories and individual researchers with our ELISA assay development services, we have managed to establish and fine-tune a thorough custom assay development procedure that takes into account every aspect of your research to deliver adaptive assay solutions for research, CE or IVD purposes. Here’s the blueprint of our custom assay services:
The best way to demonstrate our expertise in ELISA sandwich development is to share a representative case study of a biomarker assay we developed.
The aim of this project was to develop and optimize a biomarker assay to detect high levels of a biomarker specific to the early stage(s) of prostate cancer previously identified. The sample set of serum donors for validation consisted of healthy individuals, individuals with breast cancer and target individuals, i.e. individuals with prostate cancer.
Standard OHS screening protocol was deployed to identify the regulators of a common protein target of anticancer drugs. The following figure (FIGURE 1) illustrates the generic working principle behind OHS screening.
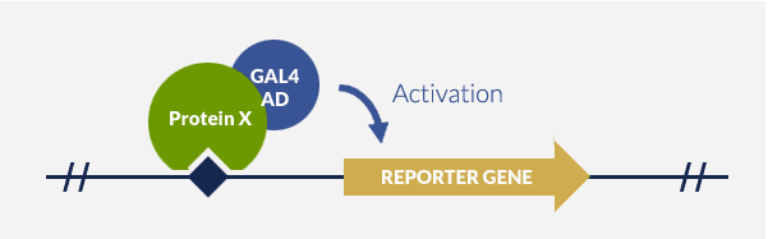
Principle of OHS system
In vivo identification of DNA-Binding protein thanks to fusion with GAL4-AD and activation of a reporter gene
The steps detailed below were followed to develop a Sandwich ELISA protocol for the biomarker discovered via OHS screening in the preliminary stage of the custom assay development project.
As described in the step 4 earlier, an antibody matching experiment resulted in a set of highly reliable data points that were tabulated, and graphically and empirically analysed to determine the most suitable pair match.
The following graph (GRAPH 1) details the matching experiment results derived from matching various antibody pairs.
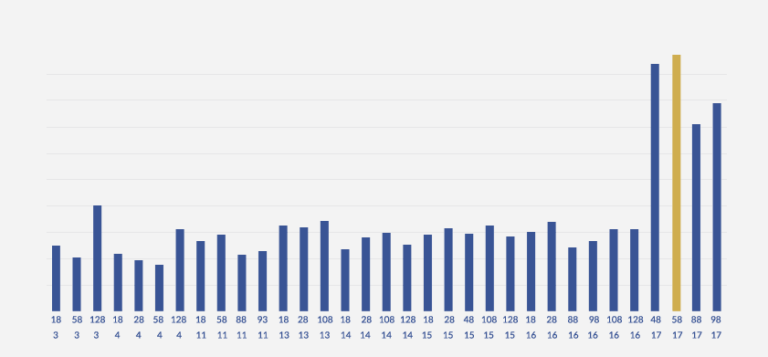
GRAPH 1: DETERMINATION OF THE BEST PAIR FOR SANDWICH ELISA
As can be clearly noticed, Detection Antibody 4B and Detection Antibody 5B exhibit remarkably good pairing with Coating Antibody 17. Among these two contenders, the pair of Detection Antibody 5B and Coating Antibody 17 was noticed to provide consistently better pairing. Thus, empirical and experimental analysis of over 90 pairs allowed us to zero in on the best pair match.
Once the best pair of antibodies is determined, using a Sandwich ELISA approach, a specifically optimized detection protocol was created. This involved the choice and usage of appropriate blocking buffers, along with suitable incubation periods, antibody dilutions and other parameters.
The following graph (GRAPH 2) plots the concentration values against the associated OD, giving us a highly reliable and accurate empirical curve that can be used in the future for extrapolation needs as a part of the complete Sandwich ELISA protocol for this biomarker assay.
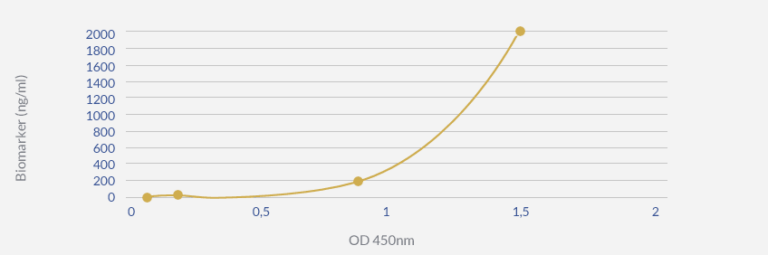
GRAPH 2: DETECTION THRESHOLD DETERMINATION IN BLOOD SAMPLES
Conclusion: this optimized Sandwich ELISA protocol allows detecting the biomarker at a concentration ≤0.2 ng/ml in patient blood samples.
The evaluation of the custom ELISA Sandwich protocol was carried out using blood samples from healthy donors, breast cancer patients and prostate cancer patients. The optimized ELISA protocol was used to assay biomarker levels in samples compared to PSA levels.
The following graph (GRAPH 3) illustrates the high levels of prostate specific biomarker in prostate cancer patients, as detected by the custom Sandwich ELISA protocol developed at ProteoGenix, enabling the categorical discrimination between non-prostate cancer patients (healthy donors and breast cancer patients) and prostate cancer patients. This discrimination was much clearer and more conclusive than when assaying PSA biomarker.
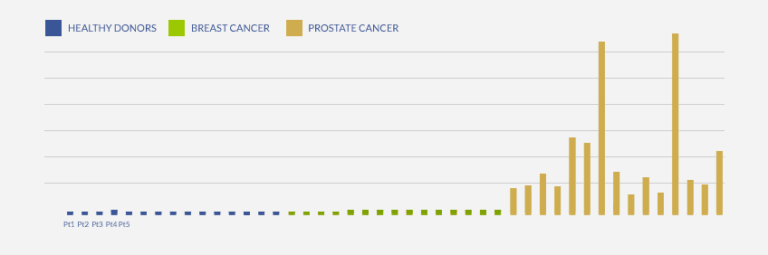
GRAPH 3: DETERMINATION OF PROSTATE-SPECIFIC ANTIGEN LEVEL IN BLOOD SAMPLES OF HEALTHY AND CANCER PATIENTS (SANDWICH ELISA)
A huge increase of Prostate-specific biomarker level is detected in prostate cancer patients
This case study represents a lot more than just facts, figures and data. Such advancement and ability to customize the assay development process – otherwise a long, tedious and meticulous task – to this degree is a great asset to have at researchers’ disposal. Custom assay development not only provides solutions tailored for your projects, but it also saves precious time, energy and other resources that you would otherwise spend on trying to make standardized assays work.
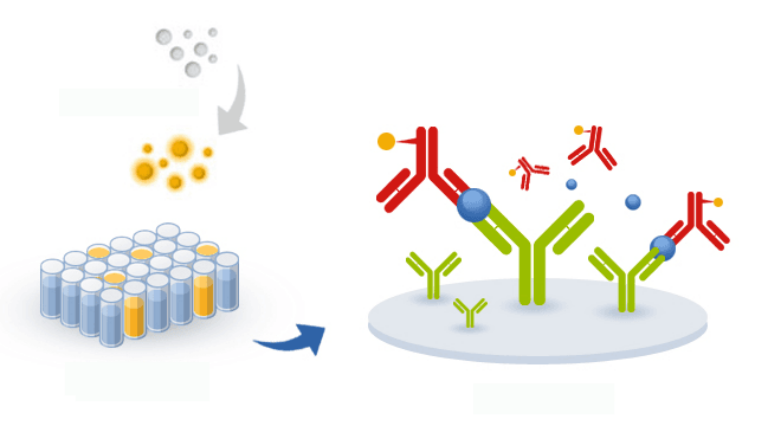
Sandwich ELISA differs from classical ELISA techniques by the adsorption of a capture antibody directly on the plate. This confers to sandwich ELISA the capacity to detect or to measure the concentration of an analyte in an impure sample (contrary to other ELISA techniques where the antigen coating is made by unspecific adsorption).
Sandwich ELISA allows for either direct or indirect detection.
Direct detection implies the use of two primary antibodies, a non-labeled one as capture reagent and a second labeled primary antibody that will be used both for capture and detection.
Indirect detection implies the use of two non-labeled primary antibodies, each recognizing a different and non-overlapping epitope of the same antigen and a secondary antibody detecting the second primary antibody (the one non coated to the plate). Indirect detection offers many advantages over direct detection as:
It does not require to label a primary antibody. Consequently, the primary antibody retains its maximum immunoreactivity.
Secondary antibodies can bind to several epitope of a primary antibody leading to signal amplification.
A wide variety of secondary antibodies are available commercially.
Polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies present different properties. While monoclonal antibodies are characterized by high specificity due to the recognition of a single epitope of an antigen, polyclonal antibodies are able to recognize several epitopes of a same antigen leading to higher cross-reactivity. Of course, this will affect the properties of your sandwich ELISA.
Choosing the appropriate clonality will depend on your goal:
If your goal is to detect a maximal amount of your target, polyclonal antibodies as capture antibodies will represent the right solution. In counterpart, the use of polyclonal antibodies as capture reagent will led to some unspecific binding. Thus, using polyclonal antibodies as capture reagent will remain the best solution if you try to detect a low concentration target in a simple sample.
The are many factors to consider when determining the optimal experimental conditions of your sandwich ELISA assay. Concerning the buffers, this includes choosing the right temperature, pH, ionic strength, detergent… ProteoGenix includes the definition of the best experimental conditions in its Sandwich ELISA development offer.
Basically, our sandwich ELISA development service comprises several phases:
Our sandwich ELISA development service includes a validation and an optimization step with your own samples. This means that the sandwich ELISA kit we deliver is fully functional for your assays.
Sandwich ELISA is usually a method to assay a protein (in blue in the chart below) in different kinds of samples (such as serum samples, tissue homogenates, cell lysates) using a pair of antibodies. The capture antibody (in green below) is adsorbed to the plastic of 96 well plates whereas the detection antibody (in red in the chart below) will allow a detection signal to be released. ELISA Sandwich allows measuring the concentration of an analyte in a complex sample thanks to the immobilized capture antigen which acts as a purification step and confers to the assay a very high specificity. In an ELISA sandwich, the detection antibody can be directly conjugated to biotin, HRP or AP (in yellow in the chart below) but it is also possible to use a conjugated secondary antibody to detect it if the coating antibody is from a different host species.